
Understanding the effects of pulse charging is vital for the practical applications of self-powered systems with TENGs. Although lots of progresses have been made on self-powered system by combing TENGs with batteries, ,, ,, , the effects of pulse charging on the performance of LIBs remains ambiguous. This form of electrical signal is very different from the galvanostatic form that is usually used in LIB tests, i.e., the galvanostatic charge-discharge (GCD). However, the output of TENG is pulse currents with high voltages. TENGs are devices based on contact-electrification effect and electrostatic induction effect, which can continuously harvest mechanical energy and convert it into electricity,. Among all efforts to harvest energy from various sources, triboelectric nanogenerators (TENGs) represent as one of the most promising technology. Recently, sustainable energy harvesting and storage is drawing more and more attention due to the emerging of brand-new, flexible and smart electronics.
#Li ion battery pulse charging frequency portable
Lithium ion batteries (LIBs) have been widely used in portable electronic devices and electric vehicles due to their low cost and high energy density over other energy storage devices, ,,. Based on these results, we further designed a better procedure by combining galvanostatic charge-discharge (GCD) mode with pulse charging mode to improve the battery performance.
#Li ion battery pulse charging frequency software
Bad cycling performance of LIBs at pulse charging modes is ascribed to the pulverization of electrode particles arising from the larger strain during cycling, which is corroborated by the software simulation. Moreover, the cycle performances of the LIBs with intermittent and continuous pulse charging were also investigated.
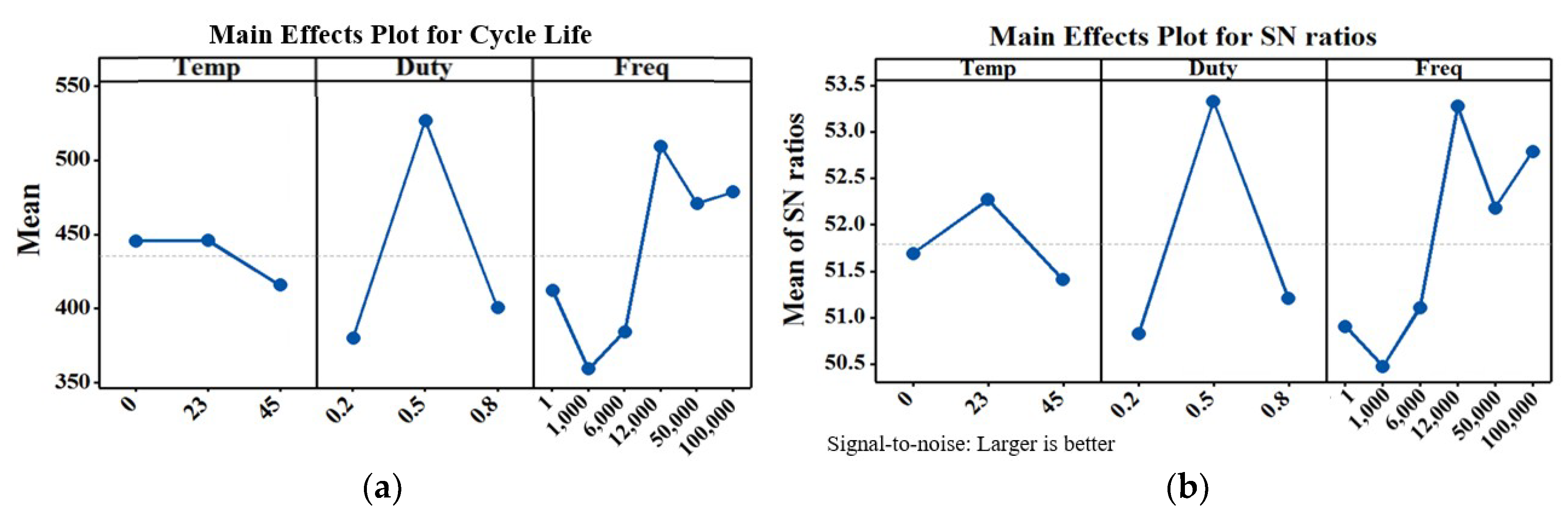
All-atom classical molecular dynamics simulations suggest that the different diffusion coefficients of Li ion in electrolyte under different applied voltage may be responsible for the different energy efficiencies. A peak value efficiency of 22.9% is observed at a pulse charging voltage of 8.0 V mode. Energy efficiency of the pulse power source coupled with a LIB at different pulse charge voltages is examined. In this work, the effects of pulse charging on lithium-ion batteries (LIBs) are investigated. Gaining insight into the effects of pulse charging on the performances of energy storage devices is very important for the practical applications of triboelectric nanogenerators (TENGs).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
